We distinguish between dip slip and strike slip hanging wall movements.
Normal fault hanging wall movement.
A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault.
Other articles where normal fault is discussed.
Thrust faults with a very low angle of dip and a very large total displacement are called overthrusts or detachments.
Faults are subdivided according to the movement of the two blocks.
An upthrown block between two normal faults dipping away from each other is a horst.
They are common at convergent boundaries.
Normal dip slip faults are produced by vertical compression as earth s crust lengthens.
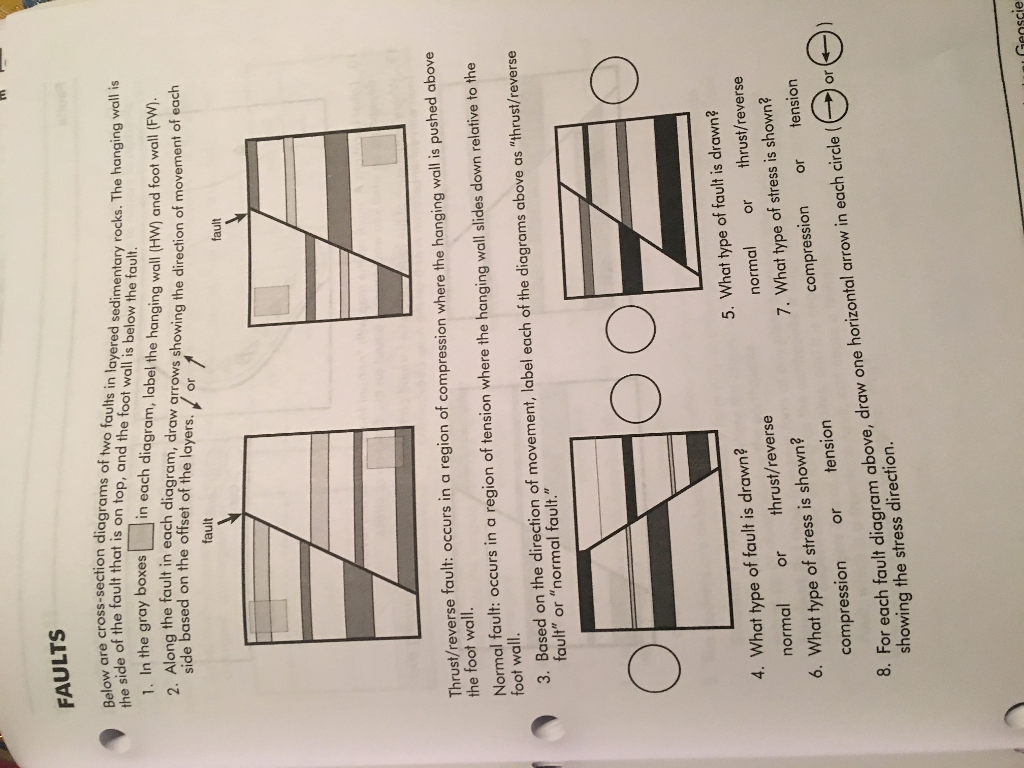
Normal faults and reverse faults are dip slip faults they experience vertical movement in line with the dip of the fault.
They are caused by extensional tectonics.
Together normal and reverse faults are called dip slip faults because the movement on them occurs along the dip direction either down or up respectively.
They are identified by the relative movement of the hanging wall and foot wall.
If the motion was down the fault is called a normal fault if the movement was up the.
They bound many of the mountain ranges of the world and many of the rift valleys found along spreading margins.
Faults showing vertical movement include tensional normal and compressional reverse faults.
There are three or four primary fault types.
In a normal fault the hanging wall moves downward relative to the footwall.
The forces creating reverse faults are compressional pushing the sides together.
Fault types three main types of faults.
The hanging wall moves up and over the footwall.
The terms hanging wall and foot wall refer to the relative position of the plates after movement.
Normal faults are common.
Low angle normal faults with regional tectonic significance may be designated detachment faults.
Dip slip movement occurs when the hanging wall moved predominantly up or down relative to the footwall.
In this type of fault the hanging wall and footwall are pushed together and the hanging wall moves upward along the fault relative to the footwall.
Reverse dip slip faults result from horizontal compressional forces caused by a shortening or contraction of earth s crust.
Economic minerals often grow along faults and these terms come from where a miner would stand and where they would hang their lantern.
Reverse faults form when the hanging wall moves up.
Tensional faults are produced through tension extension or pulling apart of the crust causing the hanging wall to move down relative to the footwall.
A dip slip fault in which the block above the fault has moved downward relative to the block.
In a normal fault the hanging wall moves downwards relative to the foot wall.
The hanging wall slides down relative to the footwall.
This is literally the reverse of a normal fault.
Faults are classified according to the direction of relative movement along the fault.
Thrust faults are reverse faults that dip less than 45.